Apple CarPlay is getting a facelift in 2024
While I’m not on the level of Grandpa Simpson, shaking my fist at the sky to bemoan technological progress, it’s hard to love the increasingly screen-heavy interiors of most new cars today. Apple CarPlay has made the connection between most smartphones and car technologies more bearable, but it’s becoming increasingly clear that the system will soon conquer all in-car technology interactions.
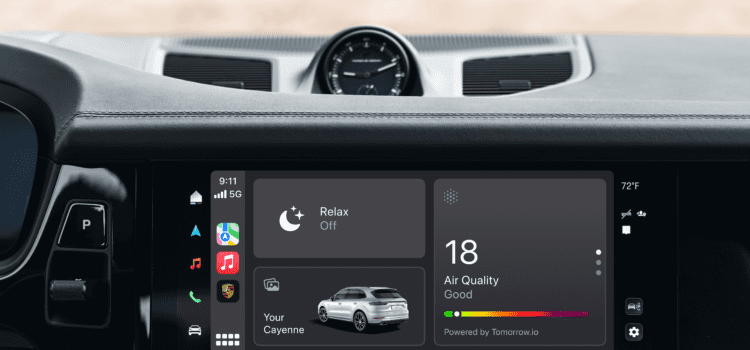
Porsche and Aston Martin recently announced updates to their in-car CarPlay interfaces, which will bring with it a far more involved system when it arrives in 2024. The new Apple interface will interact with the vehicle’s tire pressure sensors, outside thermometers, and more. Much like Android Automotive, the new CarPlay will also introduce certain UI design elements unique to specific car brands. The updates would bring a significant evolution in the system’s capabilities, but Apple will not store users’ data outside of the vehicle.

We’re not talking about a radical departure from the CarPlay interfaces we’ve seen to date. Porsche’s mockup shows a home screen with a few new displays and icons, but it’s largely the same look that has become a mainstay in new cars today.
These changes highlight a growing divide between automakers willing to embrace and progress the technology and those who feel differently. General Motors announced that it would no longer install Apple CarPlay in its new EVs, favoring Google’s services, but others have taken a softer approach, with companies like Ford saying they’d hold onto the tech. Tesla and a couple of others have never embraced the interface, instead relying on their own systems, but the car-buying public hasn’t expressed the same love for in-house systems over their preferred Apple interface.